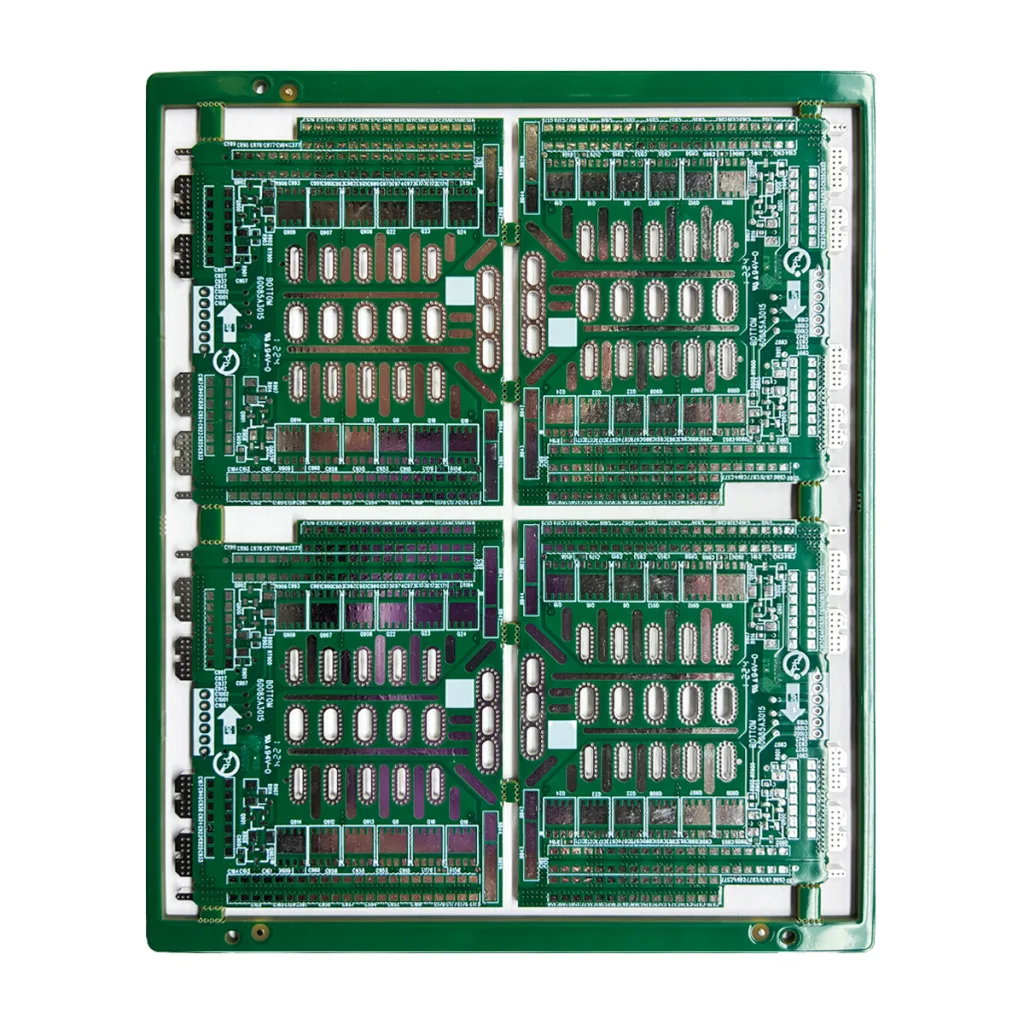
High-Reliability 8-Layer Rigid PCB Product Overview & Definition
In the realm of high-speed, high-density electronic design, multilayer PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) are indispensable. UGPCB’s 8-layer rigid PCB, built with a substantial 2.0mm board thickness and 3OZ heavy copper foil, is engineered to withstand demanding electrical and physical environments. It serves not only as the foundation for electrical connectivity but as a critical component ensuring device stability and enhanced product reliability. For applications in industrial controls, power systems, or automotive electronics, this high-specification board is the optimal solution for complex, high-performance designs.
Core Specifications
-
Layer Count: 8-Layer Rigid PCB
-
Finished Board Thickness: 2.0mm ±10%
-
Base Material: FR-4, Glass Transition Temperature (Tg) ≥ 170°C
-
Surface Finish: Lead-Free Hot Air Solder Leveling (HASL-LF)
-
Copper Weight: 3 ounces per square foot (≈105μm) for both inner and outer layers
-
Solder Mask & Silkscreen: Green LPI Solder Mask, White Silkscreen Legend
Critical Design Considerations
When designing with this high-specification PCB, engineers must prioritize:
-
Thermal Management: Leverage the high current-carrying capacity of 3OZ heavy copper to optimize power and ground planes, reducing impedance and heat rise. Use thermal simulation in conjunction with the high heat resistance of FR-4 TG170 material.
-
Impedance Control & Signal Integrity: The 8-layer stack-up allows effective separation of signal, power, and ground layers. Precise calculation and control of trace impedance (e.g., 50Ω single-ended, 100Ω differential) is essential to minimize reflection and crosstalk.
-
Mechanical & Electrical Reliability: The 2.0mm thick board enhances overall rigidity, suitable for applications with vibration or insertion stress. For high-voltage or high-current nodes, adjust trace width and clearance according to IPC-2221 standards and the 3OZ copper weight to ensure safety margins.
-
DFM (Design for Manufacturability): Collaborate with UGPCB’s engineering team early to address specific requirements for heavy copper PCB and thick board PCB processing, such as drilling parameters and plating uniformity, ensuring a high-yield manufacturing process.
How It Works & Structure
An 8-layer PCB is fabricated by laminating multiple conductive layers into a single unit using precise processes including inner-layer imaging, lamination, drilling, and plating. Electrical connections between layers are established via plated through-holes (PTHs), blind vias, or buried vias. A typical stack-up example is:
Top Layer (Signal) — Prepreg — L2 (Ground) — Core — L3 (Signal) — Core — L4 (Power) — Core — L5 (Signal) — Prepreg — Bottom Layer (Signal)
This “sandwich” structure effectively isolates high-speed signals, provides solid reference planes, and ensures efficient power distribution.
Performance & Key Features
-
Superior Electrical Performance: 3OZ heavy copper provides extremely low conductor resistance and excellent current-carrying capacity (over 3x that of standard 1OZ copper), reducing power loss and voltage drop.
-
Exceptional Thermal Reliability: FR-4 TG170 high Tg material withstands higher operating and soldering temperatures. Combined with the thermal conductivity of heavy copper, it significantly improves long-term reliability in high-temperature environments.
-
Enhanced Mechanical Stability: The 2.0mm thick board combined with rigid FR-4 offers superior resistance to bending and vibration, ideal for harsh operating conditions.
-
High Solder Joint Reliability: The HASL-LF surface finish provides a flat, coplanar pad surface with excellent solderability and extended shelf life, compliant with RoHS directives.
-
High-Density Interconnect (HDI) Capability: The 8-layer design offers ample routing space for complex circuits, facilitating device miniaturization and functional integration.
Production Process Overview
Engineering Review → Material Cutting (FR-4 TG170) → Inner Layer Imaging & Etching (3OZ) → Oxide Treatment & Lamination → Mechanical Drilling & Copper Plating → Outer Layer Patterning & Plating (to 3OZ) → Solder Mask Application (Green LPI) & Silkscreen (White) → Lead-Free HASL Surface Finish → Electrical Testing & Final Inspection (per IPC standards)
Each stage incorporates stringent quality control checkpoints to ensure every high-reliability multilayer PCB meets exact customer specifications.
Primary Applications & Use Cases
This PCB is designed for high-power, high-stability applications:
-
Industrial Control Systems: PLCs, motor drives, and industrial power supplies requiring heavy copper PCBs for high current.
-
Renewable Energy & Power Systems: Solar inverters, UPS systems, and EV charging modules relying on high current capacity and thermal endurance.
-
Automotive Electronics: On-Board Chargers (OBC), Battery Management Systems (BMS), and DC-DC converters, where high Tg PCBs are essential for under-hood temperatures.
-
Telecommunications Infrastructure: Base station power amplifier units and network backup power systems.
-
High-End Test & Measurement Equipment: Instruments requiring stable power delivery and low-noise performance.

Product Classification (Per IPC Standards)
-
By Layer Count: Multilayer PCB (>4 layers), specifically an 8-layer circuit board.
-
By Rigidity: Rigid PCB.
-
By Base Material: FR-4 PCB, subset: High Tg PCB (Tg ≥ 170°C).
-
By Special Process: Heavy Copper PCB (per IPC-2152), Thick Board PCB.
-
By Application Class: Suitable for IPC Class 2 (Dedicated Service Electronic Products) and Class 3 (High-Reliability Electronic Products) applications, including Industrial Grade PCB, Power Electronics PCB, and Automotive Grade PCB.
 UGPCB LOGO
UGPCB LOGO